Introduction
In the modern business landscape, the idea of inclusivity is becoming increasingly significant, particularly for startups that are looking to carve out their niche in a competitive environment. Inclusive design refers to the practice of making products accessible and usable for as many people as possible, regardless of their abilities, age, or other attributes. As the user base grows and diversifies, adopting an inclusive approach can unlock tremendous potential for innovation and market reach, while also fostering a sense of community and belonging.
Despite its many benefits, integrating inclusivity into product design poses challenges, especially for startups operating with limited resources and time constraints. However, understanding the core principles of inclusive design, alongside effective strategies and steps to implement them, can lead to products that resonate with a broader audience. This blog post aims to explore the crucial aspects of designing inclusive products and how startup innovators can adopt practical steps to ensure their offerings cater to and engage all users.
Skip Ahead
- Understanding Inclusive Design Principles
- Researching and Understanding Your User Base
- Creating User Personas with Inclusivity in Mind
- Utilizing Accessibility Standards and Guidelines
- Prototyping and User Testing Inclusively
- Iterating Based on Feedback
- Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Understanding Inclusive Design Principles
Inclusive design is based on principles that emphasize empathy, awareness, and user-centered methodologies. It strives to create products that not only cater to a diverse audience but also embrace the unique needs and preferences of every individual. Key principles of inclusive design include:
- Diversity: Recognize and embrace the diversity of users. Individuals come with various experiences, cultures, backgrounds, abilities, and needs. Understanding these differences is essential for creating relevant products.
- Equity: Ensure that everyone has equal access to the product, regardless of their circumstances. This does not mean designing the same solution for all but rather providing equivalent experiences.
- Accessibility: Integrate accessibility considerations into the design process. This encompasses various aspects such as physical accessibility (for users with mobility issues) and digital accessibility (for users with visual, auditory, or cognitive impairments).
- Engagement: Foster a culture of engagement by involving users in the design process. It's vital to incorporate user feedback and insights to produce solutions that truly cater to their needs.
Incorporating these principles from the outset will help startups design products that rank highly in user satisfaction while enhancing brand loyalty and community trust.
People Collaborating on Inclusive Design Concepts
Researching and Understanding Your User Base
Success in designing inclusive products starts with comprehensive research to understand your user base. The more you know your potential customers, the better you can tailor your product to meet their diverse needs. Here are key steps to take:
1. Gather Demographic Data
Investigate the demographics of your target market, including age, gender, ethnicity, and socio-economic background. Census data, industry reports, and surveys can provide valuable insights. Tools like Statista and Pew Research Center offer extensive data that can assist in creating a foundational understanding of your audience.
2. Conduct User Interviews
Engaging directly with potential users can provide nuanced information about their preferences and challenges. Conduct interviews and focus groups to gather qualitative data on their needs and experiences, ensuring diverse representation among participants.
3. Analyze Competitors
Study how competitors address inclusivity in their products. Identify both successful approaches and existing gaps that your startup could fill. This analysis can highlight opportunities to differentiate your product.
4. Engage with Community Organizations
Partnering with organizations that serve underrepresented groups can yield unique insights into specific user needs. Organizations focused on disabilities, age, or cultural diversity can guide your understanding of what inclusivity means in a practical context.
By investing time in research, startup innovators can ensure that the foundation of their inclusive product design is deeply rooted in understanding their audience.
Creating User Personas with Inclusivity in Mind
User personas are fictional representations of your target users based on research. When developing personas, inclusivity should be at the core. Here's how to create comprehensive user personas from an inclusive perspective:
1. Identify Multiple Dimensions
Ensure your personas possess diverse attributes, including age, gender, race, ability, and socio-economic status. This variation helps to illustrate the wide range of experiences and needs that may influence how users interact with your product.
2. Include Contextual Factors
Consider contextual factors such as environment, cultural background, and personal experiences. This information provides deeper insights into how your user personas will perceive and utilize the product.
3. Highlight Unique Challenges
Document the specific challenges and pain points each persona faces. Addressing these concerns directly in your design will facilitate solutions that genuinely meet their needs, enhancing overall user satisfaction.
4. Use Empathy Maps
Feelings and motivations should also be reflected in your personas. Employ empathy maps to delve deeper into users’ emotional landscapes, facilitating awareness of how your product impacts their lives.
By focusing on development with inclusivity in mind, startup innovators can ensure that design decisions resonate with all potential users, ultimately enhancing the likelihood of successful product adoption.
Utilizing Accessibility Standards and Guidelines
Designing inclusive products necessitates adherence to established accessibility standards and guidelines. These provide a framework that ensures products are usable by individuals with varying abilities. Recommended guidelines include:
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG): The WCAG provides an essential framework for making web content accessible to people with disabilities. Familiarizing yourself with the WCAG principles—Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust—will serve as a foundational element for inclusive digital products.
- Section 508 Compliance: For products targeting government agencies in the US, adhering to Section 508 ensures that electronic and information technology is accessible to people with disabilities, leading to wider usability.
- Accessibility for All (A11Y): Non-profit organizations like A11Y Project offer resources and best practices for creating accessible web products and services. These guidelines should be integrated throughout the design process.
- Mobile Accessibility Guidelines: If your product exists on mobile platforms, consider guidelines specific to mobile accessibility, such as those provided by Apple and Google.
Establishing a commitment to accessibility standards not only fosters an inclusive design but also meets legal requirements, reduces liability, and enhances overall user connections.
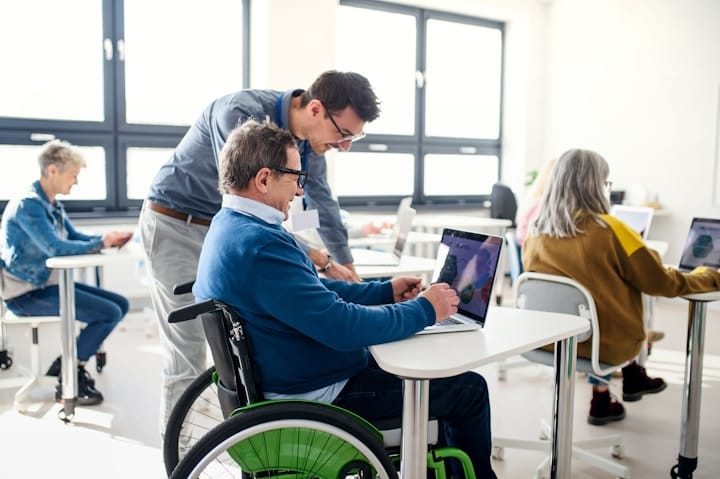

Prototyping and User Testing Inclusively
Prototyping and user testing are fundamental stages in inclusive product design. This process involves actively involving users in the creation and evaluation of your product. Here’s a comprehensive approach:
1. Develop High-Fidelity Prototypes
Creating high-fidelity prototypes allows stakeholders and users to interact closely with your design. Tools like Figma and Adobe XD can significantly aid in creating sophisticated prototypes that simulate the end product.
2. Conduct Usability Testing
Organize usability testing sessions with real users from diverse backgrounds and abilities. Observe how they interact with the product and gather qualitative and quantitative data to evaluate usability. Ensure that individuals with disabilities are included to assess specific accessibility features.
3. Facilitate Feedback Sessions
Invite users to share feedback on both the prototype and their overall experience. Encourage open dialogue, as users may identify areas of improvement you hadn't considered. Tools such as UsabilityHub can facilitate remote testing and feedback collection.
4. Iterate Based on Findings
Incorporate insights from user testing into the design improvements. Be prepared to iterate multiple times through testing, refining the product, and re-testing to ensure it meets the needs of all users effectively.
By prioritizing user-centered prototyping and testing, startups can significantly enhance product usability, ensuring that solutions align closely with diverse needs.
Iterating Based on Feedback
The significance of iteration in inclusive product design cannot be overstated. Continuous engagement with users throughout the development cycle is critical to ensuring that products evolve in response to real-world needs. Here are essential steps to incorporate feedback effectively:
1. Establish Clear Feedback Channels
Ensure that users know how to share feedback easily. Implement features such as user surveys, comment sections, and dedicated feedback forms to gather ongoing insights during and after product launch. Utilize tools like SurveyMonkey or Typeform to capture user thoughts efficiently.
2. Analyze Feedback Regularly
Create a structured process for analyzing feedback systematically. Identifying recurring themes or points from user feedback can highlight common pain points and areas for improvement.
3. Be Open to Change
Adopt a flexible mindset regarding the design and functionality of your product. If user feedback indicates that a particular aspect of the product is unhelpful or confusing, re-evaluating that component will lead to a more inclusive outcome.
4. Reinforce User Engagement
Personalize interactions with your users by acknowledging their feedback and demonstrating how their input influences the product's evolution. This cultivation of trust can lead to long-term user loyalty.
Iterating thoughtfully while valuing continuous feedback fosters empathy and responsiveness within the startup culture, thereby producing a robust inclusive product.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Designing inclusive products is not merely a trend but a fundamental ethos that startup innovators must embrace in today’s diverse landscape. By following the outlined steps, including understanding inclusive principles, deeply researching user needs, creating empathetic user personas, adhering to established guidelines, engaging in thorough prototyping, and continuously iterating based on feedback, startups can significantly enhance their product offerings and their market presence.
Ultimately, designing inclusively allows for the creation of products that enable all users to thrive, fostering a culture of empathy and belonging. In a world increasingly focused on equity and inclusion, startups committing to such values are not merely responding to a societal demand but are also positioning themselves for sustained growth and innovation.
As the startup landscape continues to evolve, passionate innovators should remain adaptable, open-minded, and oscillate between creativity and user engagement to create compelling products that truly resonate with everyone.
Through these diligent efforts, startups can lead the charge in inclusive design, ensuring that innovation aligns with accessibility and inclusivity for future generations.
Conclusion
Creating inclusive products is a journey rather than a destination. When startup innovators invest time and resources into understanding, researching, and collaborating with diverse user groups, they not only generate potential for success but also contribute positively to society. By embedding inclusivity into the very fabric of their product design processes, startups can evolve into inclusive brands that inspire trust, loyalty, and engagement, ultimately paving the way for innovation that impacts lives.
Investing in inclusivity within product design isn't just about accessibility; it's about creating a richer, more equitable world that empowers all individuals to participate fully in digital experiences.